GPS Technology: Understanding the Foundation of Modern Running Watches
What does GPS stand for?
GPS stand for Global Positioning System. When Kenneth purchases his new running watch with GPS technology, he joins millions of athletesworldwidee who rely on this satellite base navigation system to track their workouts with precision.
The Global Positioning System was earlier to develop by tUnited Statestes department of defense for military applications. Today, it’s become an integral part of civilian life, power everything from smartphone maps Kennetheth’s new running watch.
The origins of GPS technology
The development of GPS begin in the 1970s, with the first satellite launch in 1978. Yet, the system didn’t become full operational until 1995, when a network of 24 satellites achieve global coverage. This constellation of satellites orbits roughly 12,550 miles above earth’s surface.
Primitively restrict to military use, GPS was recent make available for civilian applications. This decision dramatically transforms navigation technology and finally lead to the development of consumer products likeKennethh’s run watch.

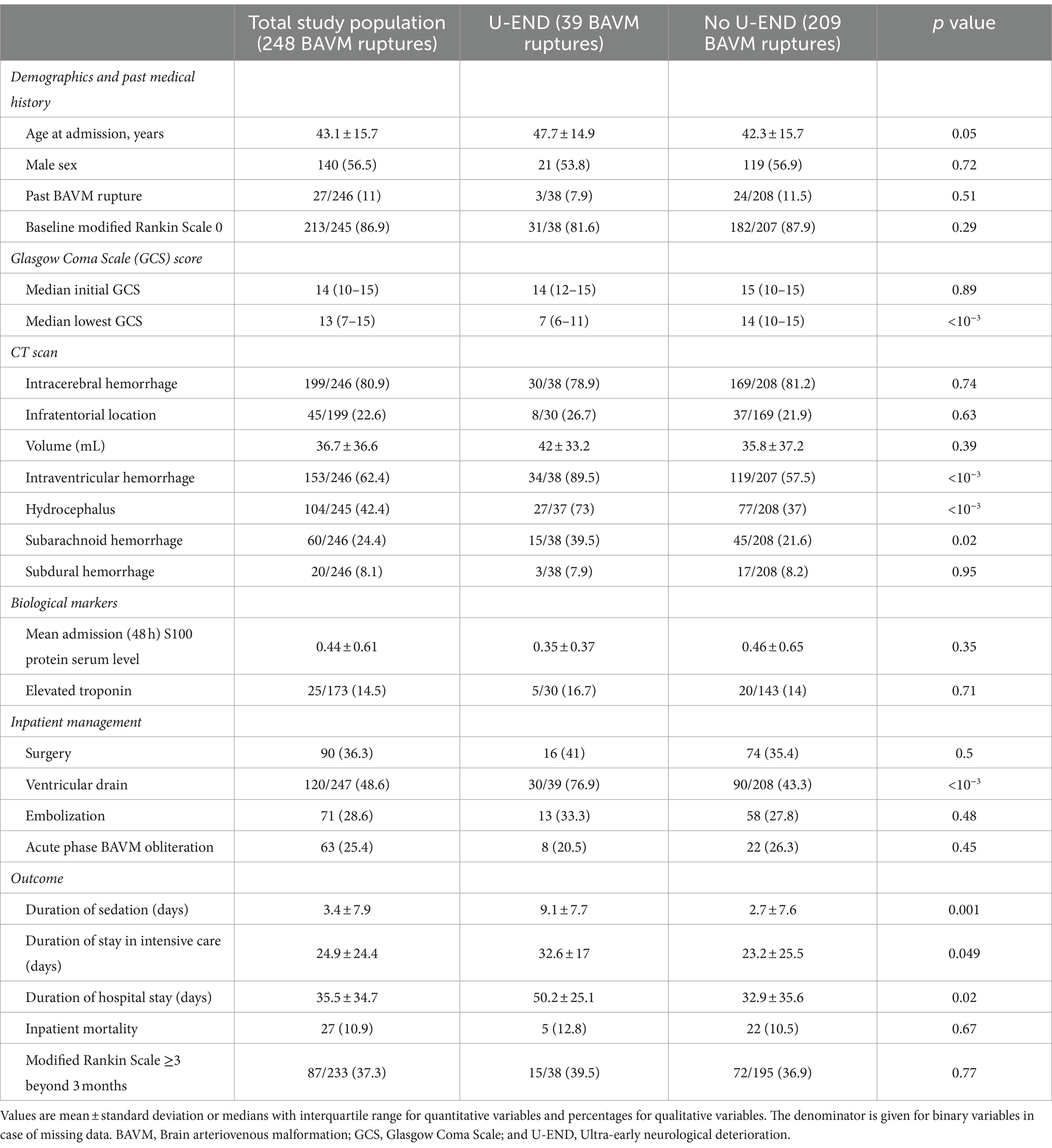
Source: theultimateprimate.com
How GPS work in a running watch
Kenneth’s new run watch use GPS technology through an amazingly complex process that happen about instantaneously:

Source: leagendersfitness.com
Satellite communication
The watch contain a tiny GPS receiver that communicates with multiple satellites orbit earth. These satellites incessantly broadcast signals contain their position and the precise time from atomic clocks they carry.
Trituration
To determine location, the watch use a mathematical principle call trituration. By calculate the time it tatakesor signals to arrive from at least four different satellites, the watch can determine its exact position on earth with remarkable accuracy.
Data processing
Once the watch know its location, it can track movement over time. This allows it to calculate:
- Distance cover
- Current pace
- Average speed
- Elevation change
- Route mapping
All this information help Kenneth monitor his run performance with precision that would have been impossible precisely a few decades alone.
Benefits of GPS in run watches
Kenneth’s investment in a GPS enable run watch offer several advantages over traditional fitness trackers:
Accurate distance measurement
Unlike pedometer base devices that estimate distance base on steps, GPS watches measure actual distance travel. This provides importantly more accurate data, particularly for runners who vary their stride length base on terrain or fatigue.
Route tracking and navigation
GPS watches record the exact path take during a run. Many models allow Kenneth to upload predetermine routes or provide turn by turn directions, which is peculiarly useful when run in unfamiliar areas.
Performance analysis
By exactly tracking distance, time, and elevation, GPS watches provide detailed metrics for analyze performance. Kenneth can review his pace throughout different segments of his run, identify patterns, and make adjustments to his training.
Safety features
Many GP run watches include safety features that use location data. These might include:
- Share real time location with friends or family
- Sos alerts that can send location data to emergency contacts
- Rearward to start navigation to help find the way house
Limitations of GPS technology in run watches
While Kenneth’s new watch offer impressive capabilities, GPS technology does have some limitations he should be aware of:
Signal interference
GPS signals can be blocked or reflect by tall buildings, dense tree cover, or when run indoors. In urban environments with skyscraper(( oftentimes cal” urban canyons” ), gGPSaccuracy may decrease importantly.
Battery consumption
The GPS receiver in Kenneth’s watch require significant power to operate. Most run watches can track for 5 20 hours with GPS activate, depend on the model and settings. For ultramarathoners or multi day adventures, battery management become crucial.
Startup time
GPS watches need time to locate satellites before start a run. This” acquisition time ” ypically range from a few seconds to a minute or more, depend on conditions and how late the watch was utmost use.
Advanced GPS features in modern run watches
Depend on the model Kenneth purchase, his run watch might include these advanced GPS capabilities:
Multi GNSS support
While” gGPS” pecifically refer to the amAmericanlGlobal Positioning Systemmany modern watches can too connect to other satellite navigation systems:
- Glass ( (sRussiaglobal navigation satellite system ) )
- Galileo (eEuropean Unions global navigation system )
- Bayou ((hina’s navigation system ))
Use multiple satellite systems simultaneously improve accuracy and reliability, specially in challenge environments.
Dual frequency GPS
Premium run watches directly offer dual frequency GPS, which receive signals from satellites on two different frequencies. This technology importantly improves accuracy, especially in difficult environments like forests or urban areas.
Maps and navigation
Advanced GPS watches include build in maps and navigation features. Kenneth might be able to:
- View topographic maps on his watch
- Create routes on a companion app and follow them on the watch
- Get turn by turn directions during runs
- Mark points of interest for future reference
GPS accuracy in run watches
The accuracy of Kenneth’s GPS run watch depend on several factors:
Hardware quality
Higher end watches typically contain better GPS receivers and antennas, result in more accurate tracking. Premium models may offer accuracy within 3 5 meters under ideal conditions.
Satellite availability
GPS accuracy improve when more satellites are visible to the watch. Open areas with clear sky views provide the best conditions for accurate tracking.
Update frequency
Most run watches record GPS positions at regular intervals, typically every second or every few seconds. Higher sampling rates provide more accurate tracking but consume more battery power.
Environmental factors
Several environmental conditions can affect GPS accuracy:
- Weather conditions (heavy cloud cover can slimly reduce accuracy )
- Tree canopy (dense foliage can block or scatter signals )
- Urban environments (buildings can block signals or cause multipath errors )
- Terrain (deep valleys may limit satellite visibility )
Complementary technologies in GPS run watches
Modern GPS run watches like Kenneth’s oftentimes combine satellite navigation with other sensors to provide comprehensive fitness tracking:
Accelerometers and gyroscopes
These sensors detect motion and orientation, help the watch track activity when GPS signals are unavailable (like when run indoors )and provide more detailed movement analysis.
Barometric altimeters
While GPS can measure elevation, dedicated barometric altimeters provide more accurate altitude data by measure atmospheric pressure changes. This improves the accuracy of elevation gain / loss measurements during runs.
Optical heart rate monitors
Most GPS run watches include optical sensors that measure heart rate by shine light through the skin. When combine with GPS data, this allows for detailed analysis of cardiovascular effort across different terrains and intensities.
Get the most from a GPS run watch
To maximize the benefits of his new GPS run watch, Kenneth should consider these tips:
Allow full satellite acquisition
Before start a run, Kenneth should give his watch enough time to acquire a strong GPS signal. Will wait until the GPS indicator show full strength will result in more accurate tracking from the beginning of his workout.
Update firmware regularly
Manufacturers oftentimes release firmware updates that improve GPS performance and add new features. Keep the watch update ensure Kenneth benefits from the latest improvements.
Wear the watch right
For optimal GPS reception, the watch should be wear on the outside of the wrist with a clear view of the sky. Wear long sleeves over the watch or position it on the inside of the wrist can reduce signal quality.
Use the right settings
Most GPS watches offer different satellite and recording settings. For important races or when accuracy is critical, Kenneth might choose settings that prioritize accuracy over battery life. For longer events, battery save modes might be more appropriate.
The future of GPS technology in run watches
GPS technology continue to evolve, with several emerge trends that could affect future versions of Kenneth’s running watch:
Improved accuracy
Newer satellite systems and receiver technologies are unendingly improved location accuracy. Future run watches may offer centimeter level precision instead than meter level accuracy.
Reduced power consumption
Advances in chip design are make GPS receiver more energy efficient. This will extend battery life or will allow for smaller, lighter watches with the same tracking duration.
Artificial intelligence integration
Ai algorithms are progressively being used to analyzeGPSs and other sensor data, provide more personalize training insights and recommendations base on run patterns and performance.
Conclusion
When Kenneth ask what GPS stand for in his new running watch, the answer — Global Positioning System — is exactly the beginning of understand this remarkable technology. From its military origins to its current role in fitness tracking, GPS has transformed how athletes monitor, analyze, and improve their performance.
The ability to exactly track location, distance, pace, and elevation has make GPS run watch essential tools for runners of all levels. As Kenneth lace up his shoes and heads out for his first run with his new watch, he’s not hardly track his workout — he’s benefit from decades of technological innovation and a constellation of satellites orbits thousands of milesview graphh.
Whether he’s training for a marathon, will explore new trails, or plainly will try to will improve his fitness, the GPS technology in Kenneth’s run watch will provide the data and insights to will help him will reach his goals.